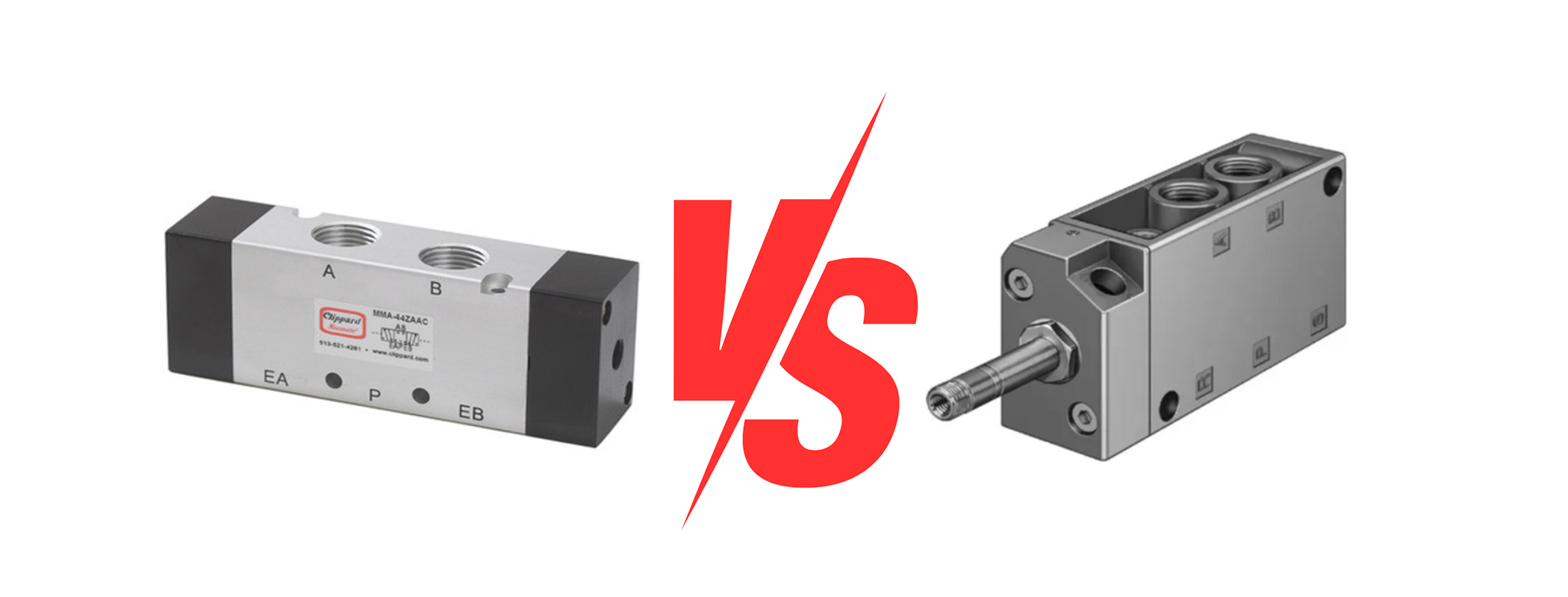
Solenoid valves and air pilot valves are two essential components in pneumatic systems, each offering distinct advantages and functionalities.
Solenoid valves, operated by an electric current, provide rapid on/off control of fluid flow, making them ideal for applications requiring quick actuation and simplified operation.
With their compact design and low power consumption, solenoid valves are versatile and well-suited for a wide range of pneumatic tasks.
On the other hand, air pilot valves utilise compressed air to control larger pneumatic devices, offering proportional control and precise positioning capabilities.
This versatility makes air pilot valves indispensable in applications where fine-tuned control and remote operation are required.
Together, these valves play integral roles in pneumatic systems, providing reliable fluid control and enabling efficient automation across various industrial applications.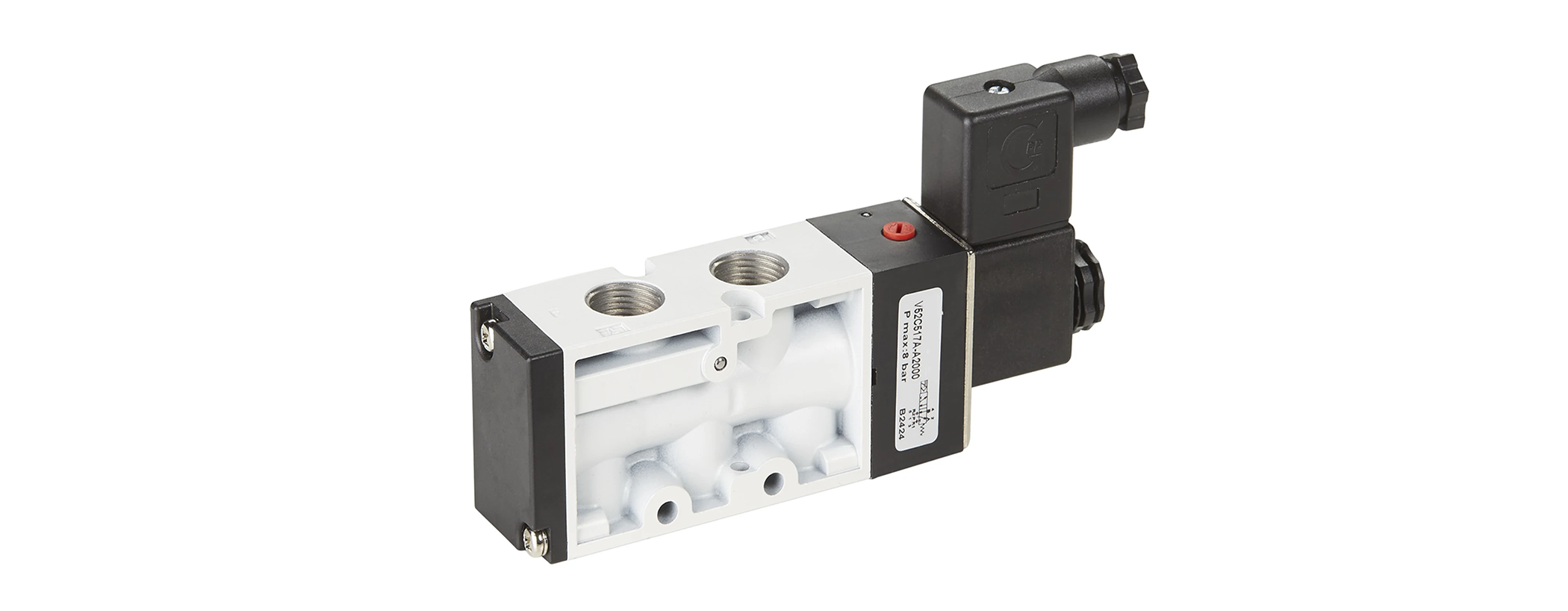
Solenoid valves play a pivotal role in pneumatic systems, offering several distinct advantages that contribute to their widespread use and versatility.
Fast Response Time: Solenoid valves offer rapid opening and closing times, facilitating quick actuation and response in pneumatic systems.
Simple Operation: They provide binary control, allowing for straightforward on/off operation in response to electrical signals, simplifying system control.
Compact Design: According to mdpi.com, solenoid valves are often compact and lightweight, making them easy to install and integrate into pneumatic systems, even in confined spaces.
Versatility: Solenoid valves are compatible with various fluids and pressures, making them suitable for a wide range of pneumatic applications, including fluid regulation, shut-off, and diversion.
Low Power Consumption: Typically, solenoid valves consume minimal electrical power during operation, contributing to energy efficiency in pneumatic systems.
Limited Flow Control: Solenoid valves provide binary control and may not offer precise control over fluid flow rates, limiting their suitability for applications requiring fine-tuned flow adjustment.
Susceptibility to Contaminants: The valve mechanism in solenoid valves may be susceptible to damage or clogging from dirt, debris, or contaminants in the fluid, affecting performance and reliability.
Potential for Coil Burnout: Continuous or frequent energizing of the solenoid coil can lead to coil overheating and burnout, necessitating replacement and causing downtime in pneumatic systems.
Noise Generation: Solenoid valves may produce audible noise during operation, which can be undesirable in noise-sensitive environments or applications.
Cost: While solenoid valves offer advantages in simplicity and ease of installation, they may be relatively more expensive compared to other types of pneumatic valves, depending on specific requirements and features needed for the application.
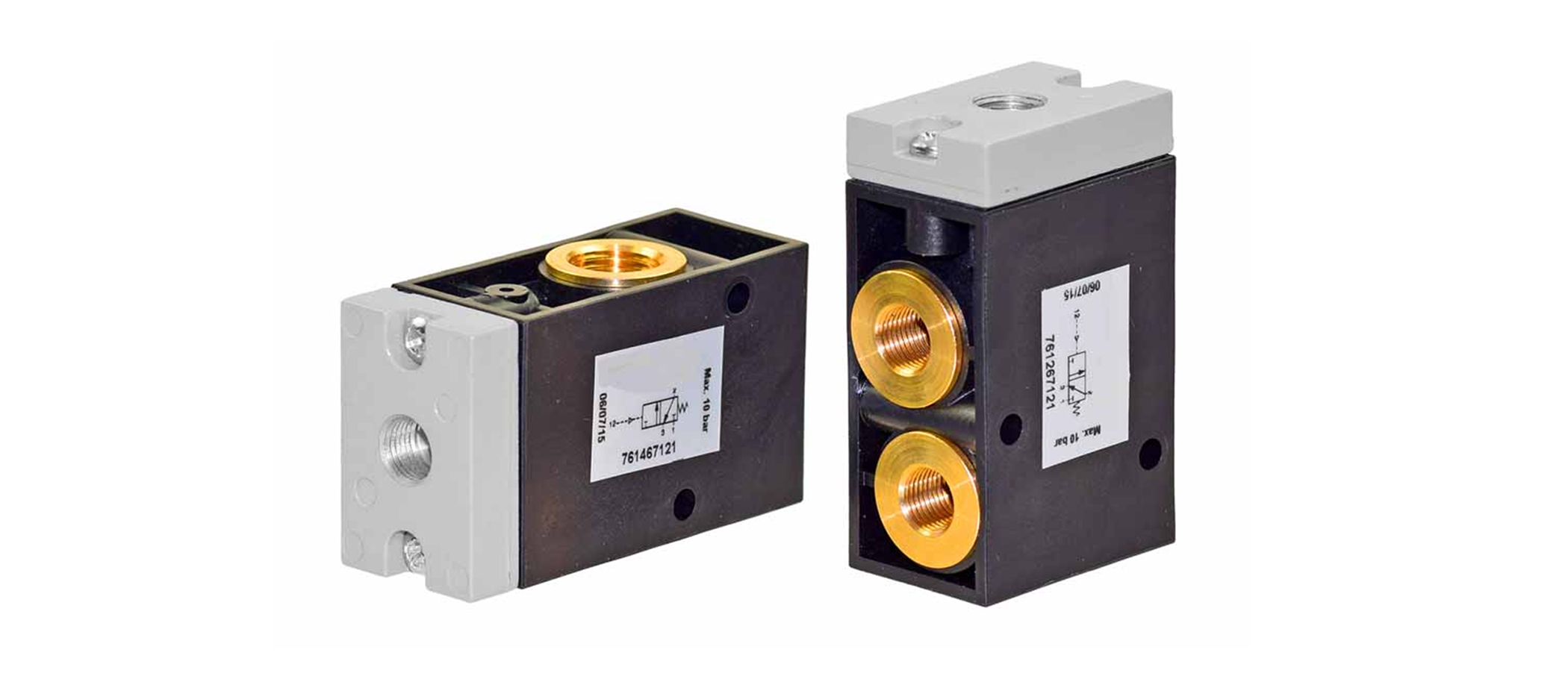

Similar to solenoid valves, air pilot valves offer several key advantages in pneumatic systems, making them indispensable components for precise control and automation.
Proportional Control: Air pilot valves offer proportional control over larger pneumatic devices, allowing for precise positioning and adjustment.
Remote Control: They enable remote control of pneumatic devices by using compressed air as a medium to transmit signals over distances, facilitating flexible system design and operation.
Versatility: Air pilot valves are suitable for a wide range of pneumatic applications, including industrial automation, robotics, and machinery control, due to their compatibility with various actuators and systems.
Safety: They are often used in safety-critical applications where reliable and precise control of pneumatic devices is essential for maintaining operational integrity and enhancing overall system safety.
Efficiency: Air pilot valves require minimal electrical power for operation, as they primarily rely on compressed air, contributing to energy efficiency in pneumatic systems.
Complexity: Air pilot valves may be more complex in design and operation compared to solenoid valves, requiring additional components and system integration, which can increase installation and maintenance complexity.
Response Time: While air pilot valves offer proportional control, their response time may be slower compared to solenoid valves, which can impact system performance in applications requiring rapid actuation.
Cost: Air pilot valves may be relatively more expensive compared to solenoid valves, particularly for systems requiring multiple valves or advanced features, which can affect overall system cost.
Maintenance Requirements: Due to their more intricate design and additional components, air pilot valves may have higher maintenance requirements compared to solenoid valves, requiring periodic inspection and servicing to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Size and Weight: Air pilot valves may be larger and heavier than solenoid valves, which can limit their suitability for applications with space or weight constraints, necessitating careful consideration during system design and installation.
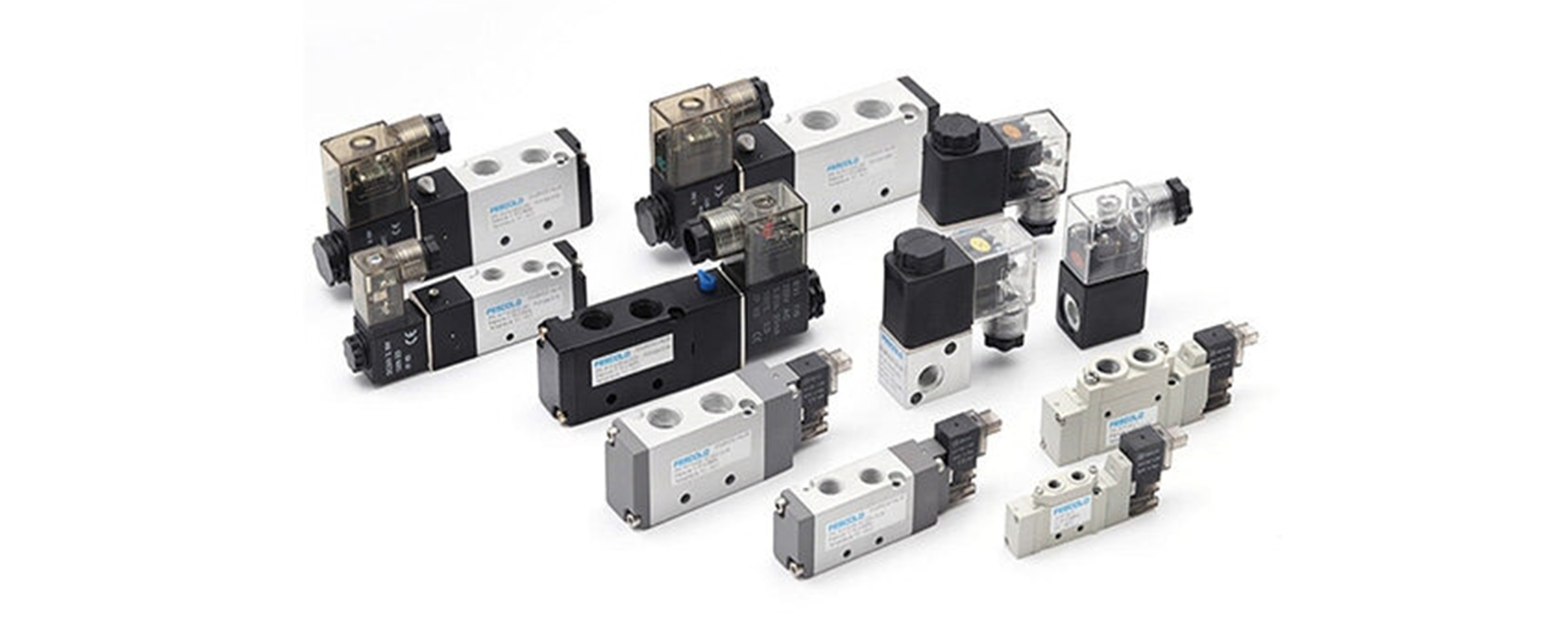

Comparing solenoid valves and air pilot valves for pneumatic systems reveals distinct differences in their operation and applications.
Operational Principle:
Solenoid valves rely on electrical signals to actuate a magnetic coil, which in turn moves a plunger to control the flow of fluid. In contrast, air pilot valves utilise compressed air to control larger pneumatic devices, with a small valve directing airflow to actuate a larger valve or actuator.
Applications:
Solenoid valves are commonly used in pneumatic systems for tasks such as fluid regulation, shut-off, and diversion, due to their compact design, fast response times, and simplicity of operation.
They are well-suited for applications where quick actuation and simplified control are paramount.
Whereas air pilot valves find applications in situations requiring proportional control and precise positioning of pneumatic actuators or valves.
They are often used in industrial automation, robotics, and machinery control, where fine-tuned control and remote operation are essential.
Solenoid valves offer advantages such as fast response times, simple operation, and compact design. However, they may have limitations in terms of susceptibility to coil burnout.
Whereas air pilot valves provide proportional control, precise positioning, and remote operation capabilities, but they are more complex and costly compared to solenoid valves.
Engineers may prefer solenoid valves over air pilot valves in certain situations, but the choice depends on the specific requirements of the application. Some of the reasons that led to preferring solenoid valve include:
Simplicity and Ease of Installation: Solenoid valves are generally simpler to install and operate as compared to air pilot valve since they only require an electrical connection for actuation. This simplicity makes them preferred in applications where quick installation and straightforward operation are important factors.
Cost: Solenoid valves are more cost-effective compared to air pilot valves, particularly for applications that do not require proportional control or precise positioning.
Fast Response Time: Solenoid valves offer rapid response times, making them suitable for applications requiring quick actuation and response.
Regardless, understanding the differences between these valve types is crucial for selecting the most suitable solution for pneumatic system design and operation.

In conclusion, the comparison between solenoid valves and air pilot valves underscores the importance of understanding their distinct features in pneumatic systems.
The choice between these valve types depends on specific application requirements and by weighing the advantages and disadvantages of the solenoid and air pilot valves, you can make informed decisions to meet your operational objectives effectively.
Alternatively, for those seeking professional assistance or specialised expertise in dealing with valves, SLSPRO stands as a reliable partner.
SLSPRO experts offer comprehensive services and provide tailored solutions and specialised services to meet the unique needs of clients across various industries
You can also browse our extensive solenoid valve selections on our website.
Get in touch with us for professional help and greater operational efficiency today!
High-quality pneumatic equipment for a stable air supply and effective pressure monitoring.
Find Out MoreHigh-quality pneumatic equipment for a stable air supply and effective pressure monitoring.
Find Out More
 Contact Us
Contact Us 